 |
 |
- Search
| Qual Improv Health Care > Volume 24(1); 2018 > Article |
|
Abstract
Purpose
The purpose of this study is to develop the Korean root cause analysis (RCA) software that can be used to systematically investigate underlying causes for preventing or reducing recurrence of patient safety incidents.
Methods
We reviewed the existing guidelines and literatures on the RCA in order to figure out the RCA process. Also we examined the existing RCA softwares for investigating patient safety incidents to design the contents and interface of the RCA software. Based on the results of reviewing literatures and softwares, we developed a draft version of the Korean RCA software that can be easily used in Korean hospital settings by RCA teams.
Results
The Korean RCA software consisted of several modules, which are modules for identifying patient safety incidents, organizing RCA team, collecting and analysing data, determining contributory factors and root causes, developing the action plans, and guiding evaluation.
Conclusion
The Korean RCA software included optimized RCA process and structured logic for cause analysis. Thus even beginners in RCA are expected to easily use this software for investigating patient safety incidents. As software has been developed with the public financial support, it will be distributed free of charge. We hope that it will contribute to facilitating patient safety improvement activities in Korea.
2016년 7월 29일 환자안전법이 시행되었다. 이 법은 항암제인 빈크리스틴(vincristine)의 투약 오류로 인하여 환자가 사망한 사건이 반복적으로 발생하자, 이에 대해 반성하여 유사한 환자안전사건(patient safety incident)이 재발하지 않도록 예방하기 위한 취지로 제정되었다. 이 법의 핵심 제도는 환자안전 보고.학습 시스템으로, 의료기관에서 발생한 환자안전사건에 대하여 의료인 등이 자율적으로 보고하고 이를 분석하여 의료기관 전체를 학습시키는 데 그 목적이 있다[1]. 의료 서비스는 의료진이 환자를 대면하여 제공하기 때문에 환자안전사건의 원인을 의료진의 잘못으로 생각하기 쉽다. 그러나 근본적으로 의료 오류의 문제는 의료진 개인의 문제라기보다는 불완전한 의료 시스템 때문에 발생한다고 알려져 있다[2]. 따라서 환자안전사건을 예방하기 위해서는 시스템의 취약점을 찾아 개선하는 것이 무엇보다 중요하다.
의료 분야에서 시스템 취약성을 찾기 위한 방법 중의 하나로 근본원인분석(root cause analysis, 이하 RCA)이 있다. RCA는 발생한 환자안전사건에 대하여 무슨 사건이 일어났는지 확인하고, 그 사건이 왜, 어떻게 일어났는지 분석하여, 유사한 사건이 발생하는 것을 예방하기 위하여 무엇을 해야 하는지 확인하는 단계별 접근법이다[3]. RCA는 본래 화학, 항공, 원자력 등 산업 공학 분야에서 설계 시스템상의 오류나 잠재적인 시스템의 결함을 확인하기 위해 개발된 방법으로[4], 의료 분야에는 1990년대 중반 미국에서 도입하여[5], 현재는 영국[6], 캐나다[7] 등 여러 국가에서 환자에게 심각한 위해를 초래한 사건에 대하여 정해진 기한 내에 RCA를 수행하도록 하고 있다.
그러나 RCA를 수행하기 위해 필수적인 팀 활동 방식과 많은 시간 및 자원의 필요는 의료기관에서 RCA를 수행하는 것을 어렵게 한다고 알려져 있다[8]. 또한, 발생한 환자 안전사건에 대하여 부적절한 하나의 근본원인만을 강조하거나, RCA를 잘못된 방향으로 수행하여 개선방안으로 사용할 수 없는 결과물을 산출해내기도 하여, RCA의 목적을 달성하지 못하기도 한다[9]. 우리나라에서도 의료기관 평가 인증 기준으로 환자에게 심각한 위해를 초래한 적신호 사건(sentinel event)에 대하여 RCA를 수행하도록 하고 있다[10]. 그러나 인증 받은 급성기 의료기관을 대상으로 조사한 결과 RCA를 수행하고 있는 기관은 61.7%에 그쳤으며[11], RCA 수행 과정에서 외국에서 보고된 바와 유사한 어려움들을 겪고 있었다[12].
미국 등에서는 이러한 문제점을 해결하고 RCA를 보다 쉽고 효율적으로 수행할 수 있도록 전문적인 소프트웨어를 개발하여 사용하고 있는데, TapRooT®, RealityCharting®, PROACT® 등이 대표적인 소프트웨어이다. 이러한 소프트웨어들은 표준화된 RCA 단계와 도구를 제공하며, 이에 대한 설명을 쉽게 찾아볼 수 있어 사용자가 RCA를 수행하는 것을 돕는다[13]. 그러나 국내 의료기관에서 이러한 소프트웨어를 사용하기에는 가격이 비싸고 영어로 되어 있다는 제한점이 있다.
따라서 이 연구에서는 국내 의료기관에서의 RCA 수행을 지원하기 위하여 한국형 RCA 소프트웨어를 개발하였으며, 소프트웨어의 주요 기능을 중점으로 기술하였다.
한국형 RCA 소프트웨어에서 적용할 RCA 수행 단계를 살펴보기 위하여 국외 주요 RCA 지침을 검토하였다. 미국의 경우 보훈청 국가환자안전센터(Veterans Affairs National Center for Patient Safety, VA NCPS)[14]와 환자안전재단(National Patient Safety Foundation, NPSF)[15], 의료기관 인증기구인 The Joint Commission[3]의 RCA 지침을 검토하였다. 영국의 경우 국가보건서비스(National Health Services)의 RCA 지침[6]과 런던 프로토콜[16]을 검토하였으며, 캐나다의 경우 캐나다 환자안전기구(Canadian Patient Safety Institute) 등 여러 기관이 협력하여 개발한 RCA 지침[7]을 검토하였다. 일본의 경우 인간공학전문가가 제안한 RCA 지침[17]을 검토하였다.
검토 내용은 RCA를 수행할 사건을 선정하는 기준과 RCA 수행 단계, 지침별 특징 및 장점을 중점적으로 살펴보고 비교하였다. 대부분의 지침에서 환자에게 사망이나 영구적인 장애 등 심각한 위해를 초래한 사건에 대하여 정해진 기한 내에 RCA를 수행하도록 하고 있었다. 또한 사용하고 있는 RCA 단계는 지침별로 적게는 4단계에서 많게는 21단계로 구분되어 있었지만, 공통되는 핵심 단계는 사건에 대한 정보를 수집하여 RCA 팀 회의를 통해 사건에서 문제점을 확인하고, 문제가 왜 발생하였는지 원인을 분석하여 이를 제거하거나 완화하기 위한 활동을 계획하고 실행하는 것이었다.
소프트웨어의 주요 기능과 인터페이스 등을 확인하기 위하여 기존에 개발되어 있는 의료용 소프트웨어를 분석하였다. 분석한 소프트웨어는 TapRooT®[18], RealityCharting®[19], PROACT®[20], Causelink®[21], Causal Diagramming Tool[22], Cause Mapping[23] 이었으며, 이 중 Cause Mapping은 별도의 소프트웨어가 아닌 엑셀 프로그램을 사용하고 있었다.
분석 내용은 소프트웨어에서 적용하고 있는 RCA 수행 단계와 단계별 사용 도구, 세부 기능 등에 대하여 중점적으로 분석하였다. 아울러, 사용자의 입장에서 인터페이스의 유용성과 편의성을 검토하였다. 각각의 소프트웨어들은 각자 독자적으로 개발한 RCA 단계를 적용하고 있었다. 단계별로 사용하고 있는 도구들 또한 독자적으로 개발하였거나, 기존의 질 개선 도구들을 변형하여 적용하고 있었다. 대부분의 소프트웨어에서 사건에 대한 정보를 입력하고 저장하는 기능과 원인 분석을 위한 인과관계도(cause and effect diagram) 등의 도식을 제공하고 있었으며, 데이터 출력 및 관리 기능도 포함하고 있었다. RCA 소프트웨어의 핵심인 원인분석 단계에서 TapRooT®에서만 정해진 논리 구조(logic)에 따라 근본원인을 확인하도록 하고 있었으며, 나머지 소프트웨어에서는 사용자가 비어있는 도식을 채워나가는 형태로 구현되어 있었다.
국외 주요 RCA 지침 검토 결과와 의료용 RCA 소프트웨어 분석 결과를 토대로 한국형 RCA 소프트웨어의 개발 방향을 확립하였다. 한국형 RCA 소프트웨어의 개발 목적은 의료기관에서 RCA를 수행하는 것을 돕기 위한 것으로, RCA가 익숙하지 않은 환자안전 담당자 또는 직원들도 쉽게 배우고 활용할 수 있도록 구현하고자 하였다. 또한, 사용자의 입장에서 쉽게 입력하고 사용할 수 있도록 편의성을 최대한 고려하여 인터페이스를 구성하고자 하였다.
이에 한국형 RCA 소프트웨어에서는 RCA 수행 단계를 최대한 간단하지만 핵심을 포함하도록 선정하여 1) 사건 조사, 2) 팀 정보, 3) 문제 발견, 4) 원인 분석, 5) 개선활동 계획 및 관리로 구성하였다. 이 중 원인 분석 단계에서는 근본원인을 확인하기 위한 논리 구조를 제공하고 있는 Tap-RooT®이 표준화된 RCA를 수행할 수 있도록 하는데 도움이 된다고 판단하여 이를 참고하여 구성하였다. 또한, 개선활동의 실행이 수일에서 수개월에 걸쳐 이루어지기 때문에 개선활동 계획과 관리를 따로 구분하였으며, RCA 사례 관리를 위해 필요한 통계 및 보고서 출력, 데이터 관리 기능도 구현하였다.
한국형 RCA 소프트웨어는 웹 기반으로 개발된 소프트웨어로 도메인을 통해 접근이 가능하다. RCA 사례에 대한 비밀 보장을 위하여 사용자 계정을 생성하여 이용할 수 있으며, 이메일과 비밀번호만으로 계정을 생성할 수 있다. 소프트웨어에 작성된 내용은 작성한 사용자 계정에서만 조회, 수정, 삭제의 권한이 주어진다.
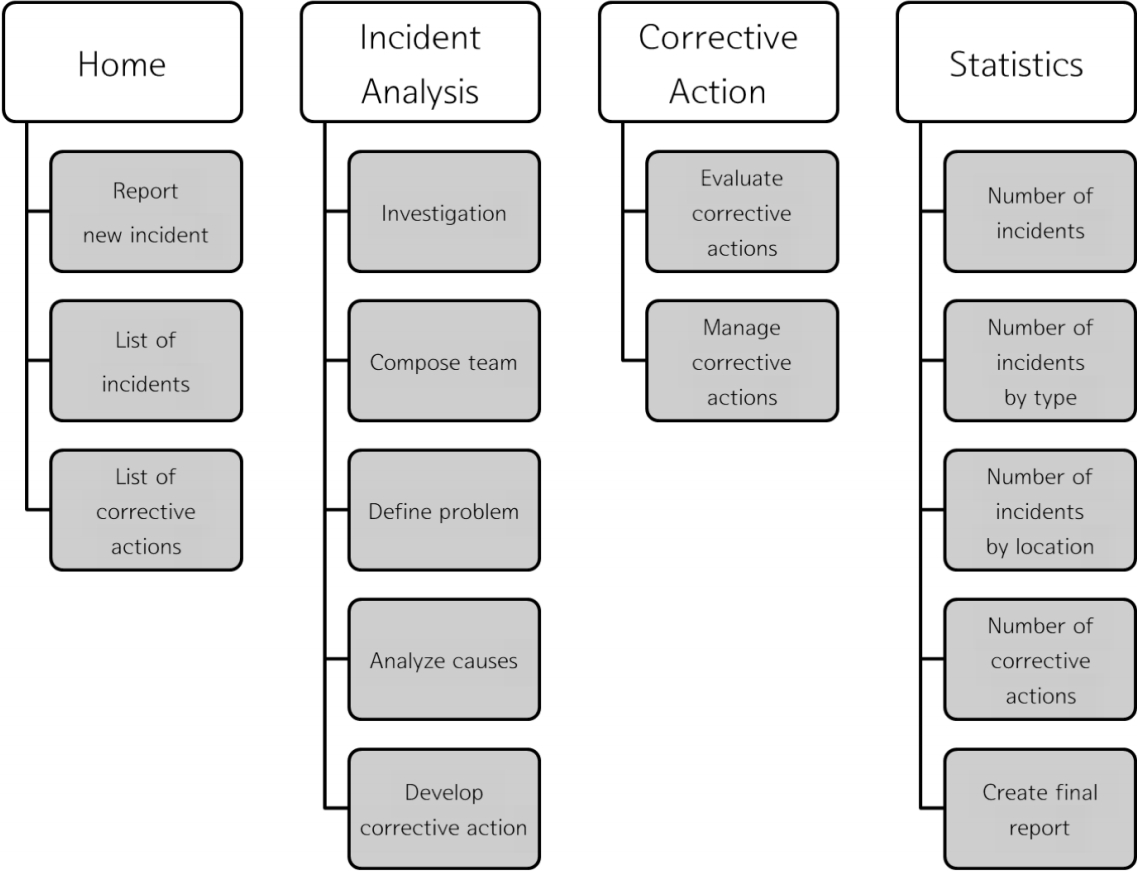
한국형 RCA 소프트웨어의 메뉴는 크게 홈화면(home), 사건 분석, 개선활동 관리, 통계 부분으로 구분된다(Figure 1). 홈화면(home)은 소프트웨어에서 처음으로 나타나는 화면으로 작성된 사건 보고서 및 개선활동 목록으로 구성되어 있다. 사건 분석에서는 사건 보고서 작성부터 개선활동 계획까지의 과정을 포함하고 있으며, 개선활동 관리에서는 실행하고 있는 개선활동들의 진행 과정을 관리할 수 있도록 하였다. 통계 부분은 사건 보고 건수 또는 RCA 수행 건수 등의 경향을 확인할 수 있도록 구현하였다. 이하에서는 각 메뉴의 세부적인 단계 및 기능을 서술하였다.
홈화면(home)에서는 지금까지 작성된 사건 및 개선활동에 대한 목록을 확인할 수 있으며, 목록에서 확인할 수 없는 경우 검색 기능을 이용하여 사건 보고서 또는 개선활동을 찾을 수 있다. 또한, 사건 목록에서는 해당 사건이 어느 단계까지 진행되었는지를 확인할 수 있으며, 클릭 한 번으로 해당 단계로 이동이 가능하게 구현하였다.
사건 분석은 사건 조사, 팀 정보, 문제 발견, 원인 분석, 개선활동 계획의 5단계로 이루어져 있으며, 해당 단계에 대한 진행 상황이 화면 상단의 바(bar)의 형태로 표현되며 단계명을 클릭하면 각 단계로 이동할 수 있다.
사건 조사 단계에서는 사건에 대한 정보를 보고서의 형태로 입력하게 된다. 사건 보고서에서는 사건 발생일자 및 장소, 사건 내용 등 사건에 대한 정보와 환자의 연령, 성별, 진단명 등 환자에 대한 정보를 입력하며, 향후 관리를 위한 사건의 결과 및 분류를 입력하도록 구성하였다. 사건 보고서의 항목은 여러 의료기관에서 사용할 것을 고려하여 현재 운영되고 있는 환자안전 보고 · 학습 시스템의 항목을 참고하여 구성하였으며, 발생 장소의 경우 개별 의료기관에서의 부서명도 필요할 것으로 판단되어 텍스트로 입력할 수 있도록 구현하였다. 아울러, 사건과 관련된 자료들을 파일의 형태로 업로드하여 보고서와 함께 관리할 수 있도록 하였다.
RCA에서 팀을 이용하는 것은 문제를 해결하는데 더 많은 창의성과 지식, 경험을 이용할 수 있다는 장점이 있다. 일반적으로 RCA 팀은 4-6명으로 관련 부서 직원으로 구성된다. 현재 개발된 한국형 RCA 소프트웨어에서는 여러 팀원들이 동시에 접속하여 소프트웨어를 사용할 수는 없지만 해당 사례 분석에 참여한 팀원들에 대한 정보를 입력할 수 있도록 하였다.
문제 발견 단계에서는 사건을 발생한 순서대로 입력하도록 하였다. 이 때 표의 형태로 각 사건의 내용, 주체, 시간, 장소를 입력하며, 사건의 번호를 조정하여 입력한 행의 순서를 변경할 수 있다. 사건의 내용 중 문제가 있다고 판단한 사건 내용에 대해서는 ‘문제’ 버튼을 클릭하여 문제로 등록할 수 있으며, 등록된 문제는 음영으로 표시하고 ‘원인 분석’ 버튼을 통해 다음 단계로 진행할 수 있다.
표의 형태로 입력된 내용은 순서도(flow chart)로 자동 구현되는데, 화면의 하단의 ‘순서도’를 클릭하면 확인이 가능하다. 순서도 화면에서도 문제를 등록 또는 해제할 수 있으며, 문제로 등록된 단계는 주황색 테두리로 표현된다.
원인 분석은 전 단계인 문제 발견에서 발견된 각각의 문제에 대하여 분석을 시행하도록 구성하였다. 원인분석은 크게 2단계로 진행되는 데 우선 사전 질문을 통하여 사건 발생에 기여한 영역들을 확인하도록 하며, 그 결과로 선택된 검토 영역에 대하여 정해진 논리 구조를 따라 원인을 분석하여 근본원인을 확인하도록 하고 있다.
사전 설문은 총 10개의 문항으로 구성되어 있으며, 각 문항에 대하여 “그렇다”라고 생각되면 선택하게 된다. 설문 등록 시 선택된 문항에 대하여 해당되는 검토 영역이 자동으로 논리 구조 도식으로 구현되어 제시되며, 이 때 문항별로 중복되는 검토 영역은 1회만 나타나게 되어 있다.
원인분석 논리 구조는 절차/지침/규정, 의사소통, 교육 및 훈련, 물리적 환경, 업무 관리, 사용 및 조작, 유지 및 관리, 질 관리, 리더십의 9개의 검토 영역으로 구성되어 있으며, 각 검토 영역은 하위 범주로 나누어져 근본원인을 찾을 수 있도록 구성되어 있다. 각각의 범주에서 노드(node)를 클릭하면 하위 범주가 생성되고, 가장 마지막의 하위 범주에 대해서 근본원인으로 선택할 수 있다. 근본원인으로 선택된 노드는 초록색 음영으로 나타나며, 개선활동 계획을 세우기 위한 다음 단계에서 근본원인으로 제시된다.
개선활동 계획 단계에서는 원인 분석 단계에서 확인된 근본원인에 대해서 개선활동을 계획하고 평가하여 최종적으로 실행할 개선활동을 선정하게 된다. 전 단계인 원인분석에서 근본원인으로 확인되는 경로를 그림으로 표현하여, 하나의 사건에서 발견된 근본원인에 대하여 종합적으로 확인할 수 있도록 하였다. 개선활동 계획을 세우기 위한 표에서는 문제 발견 단계에서 등록된 문제명과 그 문제에서 확인된 근본원인이 자동으로 구현된다. 각각의 근본원인에 대해서는 1개 이상의 개선활동 계획을 세울 수 있으며, 개선활동의 효과, 비용, 실행가능성을 평가하여 실행 또는 미실행 여부를 판단할 수 있도록 하였다.
이 연구에서는 국내 의료기관에서의 환자안전사건에 대한 RCA 수행을 지원하기 위하여 한국형 RCA 소프트웨어를 개발하였다. 이 소프트웨어는 국내 의료기관에서 접근 및 사용이 용이하도록 한국어로 개발되었으며, 표준화된 RCA단계 및 원인분석 논리 구조를 적용하였다.
일반적으로 RCA는 가시적인 원인이 아닌 숨겨져 있는 근본원인을 찾는 데 도움을 주는 단계별 접근법으로, 분석 과정에서 브레인스토밍(brainstorming), 물고기뼈 그림(fish-bone diagram) 등 여러 가지 도구들을 활용할 수 있다[24]. 이러한 방법론적인 특징은 하나의 사건에 대하여 여러 측면에서 근본원인을 발견할 수 있다는 장점이 있지만, RCA 팀 활동에 따라 동일한 사건 및 원인에 대하여 분석 과정 및 결과가 달라질 수도 있다는 단점이 있다. 호주의 한 연구에 따르면, RCA 수행에 소요되는 시간을 감안하였을 때 RCA의 최종 결과가 실제로 의도하였던 환자안전 향상을 달성하지 못하였다[25].
RCA 소프트웨어는 일정 수준 이상의 비용 효과적인 RCA의 수행을 촉진하기 위하여 그 필요성이 대두되었다. RCA 소프트웨어는 사용자들에게 표준화된 RCA 단계와 도구를 제공함으로써 RCA 과정 및 결과에 대한 타당성을 높일 수 있다. 또한, RCA 방법론에 대한 전문 지식을 제공하여 학습 시간을 단축시키고, 자료의 수집 및 분석 등을 편리하기에 만들어 RCA 팀 활동을 지원할 수 있다[26]. RCA가 처음 개발되었던 산업, 공학 분야에서는 이미 20여년 전부터 RCA 소프트웨어를 개발하려는 노력이 시작되었으며, 최근에는 다양한 RCA 소프트웨어들을 개발하여 사용하고 있다[27].
국내에서도 환자안전에 대한 관심이 높아지고, 의료기관 평가 인증으로 인하여 의료기관에서 환자에게 심각한 위해를 초래한 사건에 대하여 RCA를 수행하도록 하고 있다. 그러나 의료기관 인증을 받은 급성기 의료기관 133개 중 RCA를 수행하고 있는 기관은 61.7%에 그쳤으며, RCA를 수행하지 않는 이유로는 분석할 사건이 없음(39.1%), 시간 부족(25%), 분석 방법을 모름(17.6%), 담당자가 없음(5.5%) 순으로 나타났다[28]. 이러한 결과로 미루어 보았을 때 아직까지 국내 의료기관에서 환자안전사건에 대한 RCA의 수행이 활성화되어 있지 않다는 것을 알 수 있으며, 의료기관 평가 인증에 참여하지 않은 의료기관들은 RCA 수행비율이 비슷하거나 더 낮을 가능성이 있다.
이러한 상황에서 표준화된 RCA 단계와 원인 분석 논리 구조를 가진 한국형 RCA 소프트웨어는 국내 의료기관에서 보다 효율적으로 RCA를 수행할 수 있도록 도울 수 있다. 국내에서 많이 알려져 있는 외국의 RCA 지침은 그 단계가 세분화되어 있어 의료기관에서 따라서 수행하기가 어려울 수 있지만, 한국형 RCA 소프트웨어에 적용된 RCA 단계는 5단계로 간단하며 필수적인 내용을 포함하고 있기에 사건을 분석하는 데 충분하다. RCA의 핵심 단계인 근본원인을 확인하기 위해서 사전 설문을 통해 검토해야 할 영역들을 제시하고, 논리 구족을 통하여 근본원인을 찾도록 유도하고 있어 RCA 방법론에 익숙하지 않은 환자안전 담당자 또는 직원들도 쉽게 접근하고 학습할 수 있다는 장점이 있다. 또한 사건에 대한 정보와 자료들을 축적하여 관리할 수 있도록 함으로써 유사한 사건이 발생하였을 때 이전에 수행하였던 RCA 사례를 참고할 수 있으며, 의료기관 차원에서의 RCA 사례 관리가 용이하다.
이러한 장점들에도 불구하고 한국형 RCA 소프트웨어는 다음과 같은 제한점이 있다. 먼저, 외국의 RCA 지침과 소프트웨어를 바탕으로 개발하였기에 RCA 단계 및 원인 분석 논리 구조가 국내 의료 현황과 맞지 않는 부분이 있을 수 있다. 이에 초기 개발 버전에 대하여 국내 의료기관 환자안전 담당자를 대상으로 사용성 평가를 시행하여 소프트웨어의 내용 및 기능에 대한 의견을 수렴하여 보완해야 할 필요가 있으며, 장기적으로 국내 의료기관에서 수행한 RCA 사례들을 검토하여 그 내용을 반영해야 할 것이다. 또한, 외국의 소프트웨어와 같이 상용화하기 위해서는 근본원인분석 사례에 대한 보안 기능이 강화되어야 할 필요가 있으며, 사용자 편의성을 중점으로 소프트웨어의 구성을 향상시켜야 하겠다.
국내 의료기관에서의 RCA 수행을 지원하기 위하여 한국형 RCA 소프트웨어를 개발하였다. 이 소프트웨어는 국내 의료기관에서 사용과 접근이 편리하도록 한국어를 사용하고 있으며, 웹 기반으로 개발되었다. 또한, 아직까지 환자안전사건에 대한 RCA가 익숙하지 않은 환자안전 담당자 및 직원들을 고려하여 RCA 단계를 최적화하였고, 근본원인을 확인할 수 있는 체계적인 논리 구조를 적용하였다. 그러나 외국의 근본원인분석 지침과 소프트웨어를 기반으로 개발하였기에 향후 국내 의료기관의 근본원인분석 사례에 대한 분석을 통하여 우리나라 의료 실정에 적합하도록 원인분석 논리 구조와 기능을 보완해야 할 필요가 있다.
Ⅵ. 참고문헌
1. Patient Safety Act Article 16 [Internet]. Sejong, Korea: National Law Information Center; 2017 [cited 2017 Feb 7]. Available from: http://www.law.go.kr/lsInfoP.do?lsiS eq=167782∂efYd=20160729#0000.
2. Wachter RM. Patient safety at ten: unmistakable progress, troubling gaps. Health Aff (Millwood). 2010;29:165-73. 
3. The Joint Commission. Root cause analysis in health care: tools and techniques. 5th ed. Illinois, USA: The Joint Commission Resources; 2015.
4. Carroll JS, Rudolph JW, Hatakenaka S. Lessons learned from non-medical industries: root cause analysis as culture change at a chemical plant. Qual Saf Health Care. 2002;11(3):266-9. 
5. Bagian JP, Lee C, Gosbee J, DeRosier J, Stalhandske E, Eldridge N, et al. Developing and deploying a patient safety program in a large health care delivery system: you can’t fix what you don’t know about. Jt Comm J Qual Improv. 2001;27:522-32. 
6. National Health Service National Patient Safety Agency. Root Cause Analysis (RCA) investigation [Internet]. London, UK: NHS Improvement; 2017 [cited 2017 Nov 29]. Available from: http://www.nrls.npsa.nhs.uk/resources/collections/root-cause-analysis/.
7. Incident Analysis Collaborating Parties. Canadian Incident Analysis Framework [Internet]. Edmonton, AB: Canadian Patient Safety Institute; 2012;[cited 2017 Nov 29]. Available from: http://www.patientsafetyinstitute.ca/en/toolsResources/IncidentAnalysis/Documents/Canadian%20Incident%20Analysis%20Framework.PDF.
8. Braithwaite J, Westbrook MT, Mallock NA, Travaglia JF, Idedma RA. Experiences of health professionals who conducted root cause analyses after undergoing a safety improvement program. Qual Saf Health Care. 2016;15(6):393-9. 
9. Wu AW, Lipshutz AK, Pronovost PJ. Effectiveness and efficiency of root cause analysis in medicine. JAMA. 2008;13(6):685-7. 
10. Ministry of Health and Welfare, Korean Institute for Healthcare Accreditation. 2016 the Act on Patient Safety practice manual. Seoul, Korea: Korean Institute for Healthcare Accreditation; 2016.
11. Shin HH. Investigation and promotion of patient safety actions at medical institutions. Seoul, Korea: Korean Institute of Hospital Management; 2015.
12. Choi EY. Experiences of Patient Safety Managers in Root Cause Analysis in Korea. [dissertation]. Ulsan: Ulsan University; 2017.
13. Choi EY, Lee HJ, Ock M, Jo MW, Lee SI. Comparison of Root Cause Analysis Software for Investigating Patient Safety Incidents. Qual Improv Health Care. 2017;23(1):11-23. 
14. Veterans Administration National Center for Patient Safety. Root cause analysis tools. Root cause analysis (RCA) step-by-step guide [Internet]. Washington DC, USA: US Department of Veterans Affairs; 2017 [cited 2017 Nov 29]. Available from: https://www.patientsafety.va.gov/docs/joe/rca_step_by_step_guide_2_15.pdf.
15. National Patient Safety Foundation. Improving root cause analysis and actions to prevent harm [Internet]. Boston, USA: National Safety Foundation; 2015 [cited 2017 Nov 29]. Available from: http://www.ihi.org/resources/Pages/Tools/RCA2-Improving-Root-Cause-Analyses-and-Actions-to-Prevent-Harm.aspx.
16. Imperial College London. Systems Analysis of Clinical Incidents: The London Protocol [Internet]. London, UK: Imperial College London; 2017 [cited 2017 Nov 29]. Available from: http://www.imperial.ac.uk/media/imperial-college/medicine/surgery-cancer/pstrc/londonprotocol_e.pdf.
17. Kawano R. Improvement for medical System by Analyzing Fault root in human ERror incident. Lee MJ, translator. Seoul, Korea: HanEon; 2014.
18. Lee HY, Choi EY, Ock M, Lee SI. Guidelines for Performing Root Cause Analysis. Qual Saf. 2017;23(1):25-39. 
19. TapRooT® homepage [Internet]. Tennessee, USA: TapRoot; 2017 [cited 2017 Mar 24]. Available from: http://www.taproot.com/.
20. Apollo Root Cause Analysis™ homepage [Internet]. Ocean Grove, Australia: Apollo Root Cause Analysis; 2017 [cited 2017 Mar 24]. Available from: http://www.realitycharting.com/.
21. Reliability Center Inc. PROACT® Root Cause Analysis homepage [Internet]. Virginia, USA: Reliability Center Inc; 2017 [cited 2017 Mar 24]. Available from: http://www.reliability.com/index.html.
22. Outcome Engenuity homepage [Internet]. Minnesota, USA: Outcome Engenuity; 2017 [cited on 2017 Mar 28]. Available from: https://www.outcome-eng.com/.
23. Think Reliability homepage [Internet]. [cited on 2017 Mar 28]. Available from: https://www.thinkreliability.com/.
24. Rooney JJ, Heuvel LNV. Root cause analysis for beginners. Quality Progress. 2004;37(7):46-53.
25. Taitz J, Genn K, Brooks V, Ross D, Ryan K, Shumack B, et al. System-wide learning from root cause analysis: a report from the New South Wales Root Cause Analysis Review Committee. Qual Saf Health Care. 2010;19(6):e63. 
26. Hirsch KA, Wallace DT. Software facilitation of root cause analysis in healthcare organizations. J Healthc Risk Manag. 2000;20(1):32-5. 
27. Hussin H, Ahmed U, Muhammad M. Critical success factors of root cause failure analysis. Indian J Sci Technol. 2016;9(48):1-10. 
28. Shin HH. Investigation and promotion of patient safety actions at medical institutions. Seoul, Korea: Korean Institute of Hospital Management; 2015.